Understanding the NEC 125 % Safety Factor
The National Electrical Code (NEC) treats a kiln as a continuous load, meaning the circuit must be sized 25 % above the kiln’s maximum amperage. In practice, you start every calculation by multiplying the kiln’s full-load amps by 1.25 to create that margin of safety — protecting wiring, breakers, and your studio from overheating or nuisance trips.
Calculating Full-Load Amps for Your Kiln
Locate the amperage rating on the kiln’s data plate or spec sheet. For example, the JD230-JH draws 57 A at full power. Multiply:
57 A × 1.25 = 71.25 A.
This figure serves as the basis for all subsequent decisions.
Choosing the Correct Breaker & Fuse Size
Breakers and fuses come in standard steps (60 A, 70 A, 80 A, etc.). After applying the 125 % rule, round up to the next standard size. With 71.25 A in our example, the right choice is an 80-amp breaker or fuse. Never round down; undersized protection will trip constantly and may overheat.
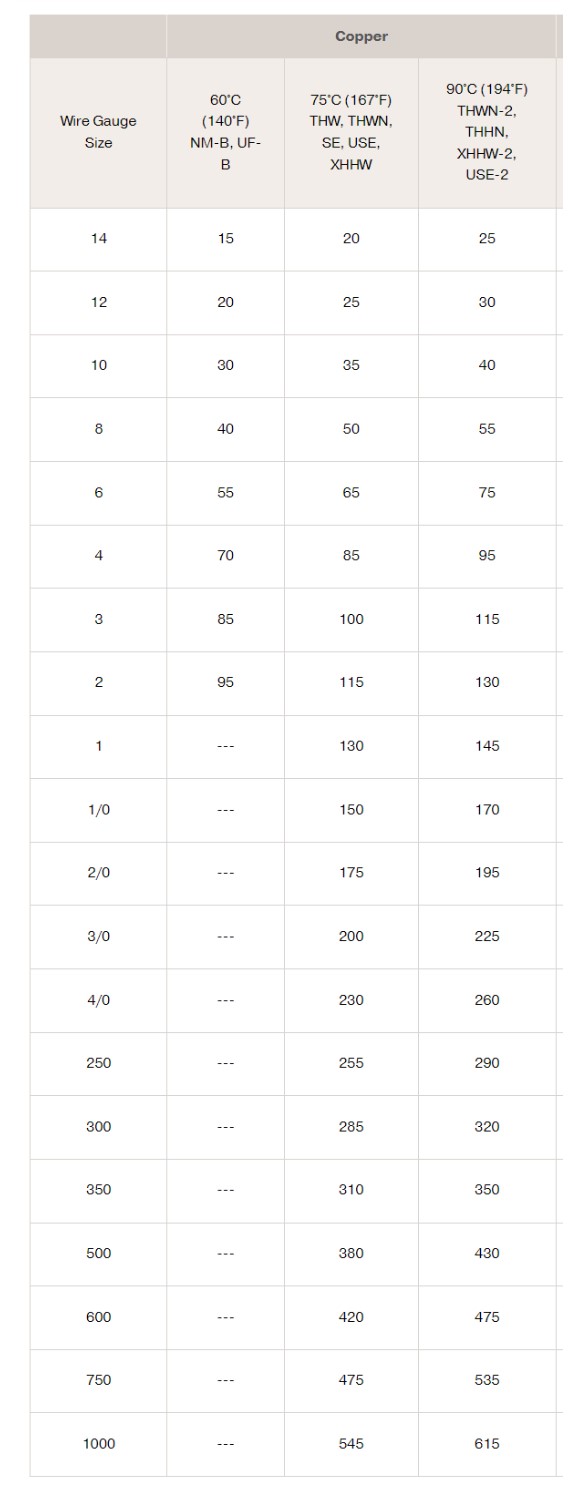
Selecting Copper Wire Gauge
Wire must also carry the 125 % load. Using the worst-case 60 °C column of the NEC table, #4 AWG copper is limited to 70 A, which is just under 71.25 A — so strictly by that rating you would step up to #3 AWG. However, most modern branch wiring is THHN or THWN-2 (75 °C/90 °C). Under the 75 °C rating, #4 AWG is good for 85 A, comfortably above 71.25 A, so #4 copper THHN is acceptable and easier to pull through conduit. Always:
- Use copper conductors (never aluminum to the kiln).
- Match conductor temp rating to the device lugs and breaker rating.
- Keep conduit fill below 40 % for easier heat dissipation.
Online Tools for Long-Run Wire Sizing
Voltage drop becomes critical when the kiln is far from the panel. Free calculators such as WireSizeCalculator.net let you enter distance, phase, amperage (use the 125 % number), and conductor type to confirm the gauge needed to keep voltage drop under 3 %. This extra check prevents sluggish firings and premature element wear.
Quick Checklist
- Find kiln full-load amps.
- Multiply by 1.25 to get required circuit amps.
- Select the next-size breaker/fuse above that value.
- Choose copper wire gauge rated for at least the same amps at the temperature rating that matches your terminals.
- Verify long runs with a voltage-drop calculator.
- Consult a licensed electrician to review local code nuances before energizing your kiln.
Follow these steps and your kiln will fire safely, efficiently, and in full compliance with the NEC.
Note: We use 75 °C wire for purposes of calculating the typical wire gauge connection side in our kiln specifications.